The Secret Life of Trees: Understanding Common Tree Diseases and How to Save Your Trees

Outline of the Article
- Introduction
- The Importance of Trees in Our Ecosystem
- Why Understanding Tree Diseases Matters
- Common Tree Diseases
- Fungal Diseases
- Oak Wilt
- Dutch Elm Disease
- Bacterial Diseases
- Fire Blight
- Bacterial Leaf Scorch
- Viral Diseases
- Mosaic Virus
- Cherry Leaf Roll Virus
- Parasitic Diseases
- Mistletoe
- Root-Knot Nematodes
- Fungal Diseases
- Signs and Symptoms of Tree Diseases
- Visible Symptoms
- Leaf Discoloration
- Canker Development
- Non-Visible Symptoms
- Stunted Growth
- Premature Leaf Drop
- Visible Symptoms
- Diagnosis of Tree Diseases
- Visual Inspection
- Laboratory Testing
- Consulting Arborists
- Preventative Measures
- Proper Tree Planting Techniques
- Pruning and Maintenance
- Soil Management
- Treatment Options for Tree Diseases
- Chemical Treatments
- Fungicides
- Bactericides
- Organic Treatments
- Neem Oil
- Compost Tea
- Mechanical Treatments
- Pruning
- Root Barriers
- Chemical Treatments
- Case Studies of Successful Tree Disease Management
- Saving the American Elm
- Rescuing Oak Trees from Oak Wilt
- The Role of Professional Arborists
- When to Call an Arborist
- What to Expect from a Professional Tree Inspection
- Long-Term Tree Health Strategies
- Choosing Disease-Resistant Species
- Regular Health Monitoring
- Community Involvement
- Conclusion
- Recap of Key Points
- The Importance of Vigilance and Proactive Care
- FAQs
- How can I tell if my tree is sick?
- What are the most common tree diseases?
- Can tree diseases be prevented?
- How often should I inspect my trees?
- When is it time to remove a diseased tree?
Introduction
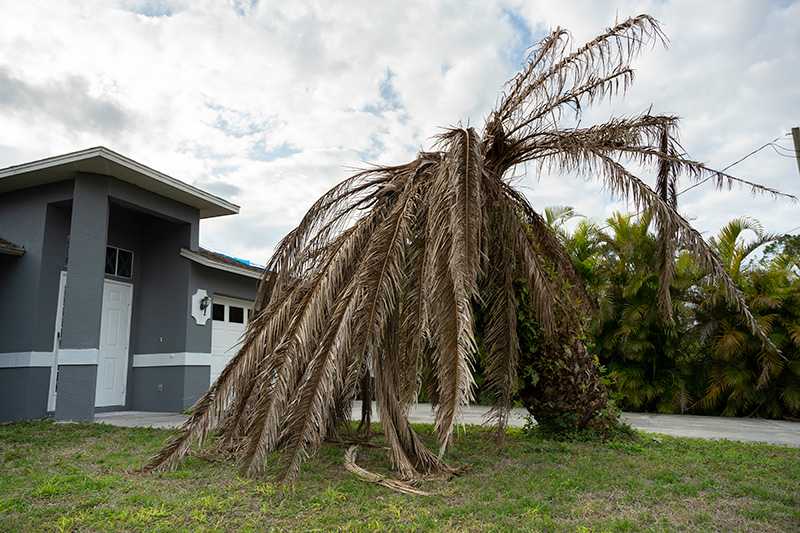
Trees are the silent sentinels of our planet. They provide shade, oxygen, and habitats for countless species while enhancing the beauty of our landscapes. However, these giants are not invincible. Just like any living organism, trees are susceptible to diseases that can threaten their health and longevity. Understanding these diseases and how to combat them is crucial for anyone who values the green giants in their backyard or community.
Common Tree Diseases
Fungal Diseases
Oak Wilt
Oak Wilt is a deadly fungal disease affecting oak trees, caused by the fungus Bretziella fagacearum. It spreads through interconnected root systems and beetle vectors, causing leaves to wilt and die.
Dutch Elm Disease
This disease is caused by the fungi Ophiostoma ulmi and Ophiostoma novo-ulmi, which spread via elm bark beetles. It disrupts water flow, leading to yellowing leaves and branch dieback.
Bacterial Diseases
Fire Blight
Fire Blight, caused by Erwinia amylovora, affects apple and pear trees. It manifests as blackened, burnt-looking branches and oozing cankers.
Bacterial Leaf Scorch
This disease is caused by Xylella fastidiosa, leading to leaf browning and scorch-like symptoms. It affects various hardwood species, including oaks and maples.
Viral Diseases
Mosaic Virus
Mosaic Virus causes mottled or streaked leaves in a variety of trees, leading to reduced photosynthesis and stunted growth. It spreads through insect vectors and contaminated tools.
Cherry Leaf Roll Virus
Affecting cherry trees, this virus leads to leaf distortion and premature leaf drop. It is spread by nematodes and grafting infected plant material.
Parasitic Diseases
Mistletoe
Mistletoe is a parasitic plant that attaches to host trees, siphoning off water and nutrients. While often seen as decorative, it can severely weaken trees over time.
Root-Knot Nematodes
These microscopic worms attack the roots of trees, causing galls and reducing the tree’s ability to absorb water and nutrients. They are particularly troublesome in sandy soils.
Signs and Symptoms of Tree Diseases
Visible Symptoms
Leaf Discoloration
Changes in leaf color, such as yellowing or browning, can indicate various diseases. It’s essential to identify whether the discoloration is due to disease or other factors like nutrient deficiency.
Canker Development
Cankers are dead, sunken areas on branches or trunks, often oozing sap. They can be a sign of fungal or bacterial infection and can girdle branches, leading to dieback.
Non-Visible Symptoms
Stunted Growth
If a tree is not growing as expected, it might be battling an unseen disease. Slow growth can result from root infections or systemic diseases.
Premature Leaf Drop
Early leaf fall can be a symptom of stress caused by diseases such as Dutch Elm Disease or Bacterial Leaf Scorch.
Diagnosis of Tree Diseases
Visual Inspection
A thorough visual inspection can often reveal telltale signs of disease. Look for symptoms like leaf spots, cankers, and abnormal growth patterns.
Laboratory Testing
For accurate diagnosis, samples of affected parts can be sent to a laboratory. Tests can identify specific pathogens, guiding effective treatment plans.
Consulting Arborists
Professional arborists have the expertise to diagnose tree diseases accurately. They can provide tailored advice on treatment and prevention.
Preventative Measures
Proper Tree Planting Techniques
Planting trees correctly can prevent many diseases. Ensure proper spacing, choose the right species for your area, and avoid damaging roots during planting.
Pruning and Maintenance
Regular pruning removes diseased branches and improves air circulation, reducing the risk of infections. Always use sanitized tools to prevent spreading pathogens.
Soil Management
Healthy soil promotes robust tree growth. Regularly test soil and amend it with organic matter to maintain nutrient levels and proper pH.
Treatment Options for Tree Diseases
Chemical Treatments
Fungicides
Fungicides can manage fungal infections when applied correctly. It’s crucial to follow label instructions and apply treatments at the right time.
Bactericides
These chemicals target bacterial infections. They can be effective when disease is detected early and applied systematically.
Organic Treatments
Neem Oil
Neem oil is a natural fungicide and insecticide. It’s useful for treating various tree diseases without harming beneficial organisms.
Compost Tea
This organic solution enhances soil health and boosts tree immunity, helping them fight off diseases naturally.
Mechanical Treatments
Pruning
Removing infected branches prevents the spread of disease within the tree. Make clean cuts and sanitize tools between uses.
Root Barriers
Installing root barriers can prevent the spread of root diseases. They are particularly effective against invasive species like root-knot nematodes.
Case Studies of Successful Tree Disease Management
Saving the American Elm
American Elms were nearly wiped out by Dutch Elm Disease. Through resistant cultivars and rigorous management, many elms have been saved and restored to urban landscapes.
Rescuing Oak Trees from Oak Wilt
In areas hit by Oak Wilt, a combination of chemical treatments, root barriers, and removal of infected trees has helped control the spread and save healthy oaks.
The Role of Professional Arborists
When to Call an Arborist
If you notice signs of disease or if your tree’s health is declining without an obvious cause, it’s time to call an arborist. Early intervention can save trees and prevent further damage.
What to Expect from a Professional Tree Inspection
Arborists will conduct a thorough assessment, including visual inspection, soil testing, and possibly lab tests. They will provide a diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your tree’s needs.
Long-Term Tree Health Strategies
Choosing Disease-Resistant Species
Planting disease-resistant tree species can prevent future problems. Research and select varieties known for their resilience in your area.
Regular Health Monitoring
Regularly inspect your trees for early signs of trouble. Prompt action can often nip problems in the bud before they become severe.
Community Involvement
Community tree planting and care initiatives can foster healthier urban forests. Participating in local programs helps ensure a collective effort in maintaining tree health.
Conclusion
Trees are invaluable to our environment and well-being, but they require care to thrive. Understanding common tree diseases and implementing preventative and treatment measures can save your trees and preserve their beauty and benefits. By being vigilant and proactive, you can ensure your trees remain healthy and robust for generations to come.
FAQs
How can I tell if my tree is sick?
Look for symptoms like leaf discoloration, cankers, stunted growth, and premature leaf drop. A professional arborist can provide an accurate diagnosis.
What are the most common tree diseases?
Common tree diseases include Oak Wilt, Dutch Elm Disease, Fire Blight, Bacterial Leaf Scorch, Mosaic Virus, and Root-Knot Nematodes.
Can tree diseases be prevented?
Yes, through proper planting techniques, regular pruning, soil management, and selecting disease-resistant species, many tree diseases can be prevented.
How often should I inspect my trees?
Inspect your trees at least once a season and after major weather events.
When is it time to remove a diseased tree?
If a tree poses a hazard or if the disease cannot be controlled and is spreading to other trees, removal might be necessary. Consult with a professional arborist for the best course of action.